Sweden Officially Became 32nd Member of NATO

Why in News?
After a prolonged struggle, Sweden official entered into North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) as 32nd member. This move carries significant implications for both Sweden and the international community.
Let’s explore the impact of Sweden’s entry into NATO, the significance of this decision, and why countries like Turkey and Hungary have opposed Sweden’s membership.
Impact of Sweden's Entry into NATO:
- Security: Sweden’s entry into NATO strengthens collective defence capabilities in the region, providing a sense of security and stability.
- Alliances: By aligning with NATO, Sweden solidifies its partnerships with other member countries, fostering cooperation in various defence and security matters.
- Deterrence: The presence of Sweden in NATO acts as a deterrent against potential aggressors, enhancing the overall defence posture of the alliance.
- Crisis Response: Sweden’s integration into NATO enables quicker and more efficient responses to crises and threats in the region.
Significance of Sweden for NATO
- Geopolitical Position: Sweden’s strategic location in the Baltic Sea region enhances NATO’s presence and influence in Northern Europe.
- Strength in Numbers: With Sweden on board, NATO gains another capable and technologically advanced member, further bolstering its military capabilities.
- Unity: Sweden’s inclusion fosters greater unity and cohesion within NATO, strengthening the alliance’s collective defence mechanism.
- Diplomatic Relations: Sweden’s membership enhances NATO’s diplomatic ties with non-member countries, facilitating broader international cooperation.
Recent Post
`
- Sociological Perspectives on Family
- Classical Languages
- Lateral Entry into Civil Services
- National Space Day
- Important National Awards of India
- Ethics Practice Case Study – 2
- Citizenship Amendment Act, 2019: Implications and Controversies
- CUTLASS EXPRESS 24: Joint Naval Exercise
- Ethics Case Study – 1
- Elementor #1103
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- NATO, established in 1949, is a military alliance comprising 32 member countries.
- Its primary mission is collective defense, with an ‘attack on one member considered an attack on all.’
- India is not a member of NATO.
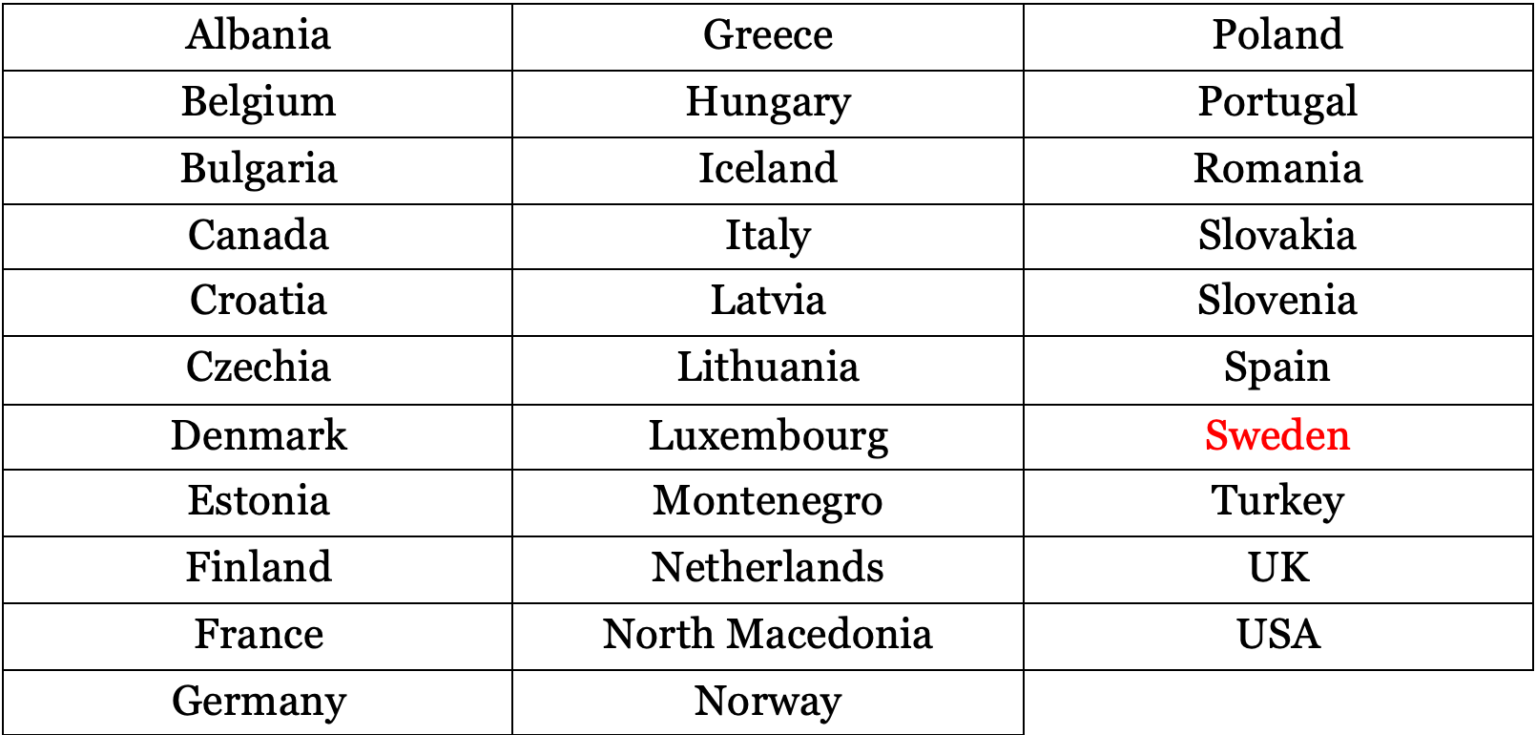
- Its member countries are:
Practice Questions
- Prelims Questions
- Mains Questions
Q1. Which among the following is NOT a member of NATO?
(a) Bulgaria
(b) Finland
(c) Latvia
(d) Bosnia
Q2. Which of the following is NOT a NATO operation?
(a) Peacekeeping in the Balkans
(b) Counterterrorism efforts in Afghanistan
(c) Space exploration missions
(d) Maritime security operations in the Mediterranean
Q3. What does NATO’s Partnership for Peace program involve?
(a) Facilitating security cooperation with member countries
(b) Encouraging economic development
(c) Facilitating security cooperation with non-member countries
(d) Providing humanitarian assistance
- How does India’s participation in NATO’s Partnership for Peace program reflect its evolving foreign policy priorities and strategic engagements on the global stage, particularly in light of its traditionally non-aligned stance during the Cold War era? (10marks, 150words)
- Analyze the potential implications and strategic advantages for both India and NATO in deepening their cooperation on maritime security initiatives, considering India’s growing geopolitical influence in the Indian Ocean region and NATO’s efforts to address security challenges beyond the Euro-Atlantic area. (10marks, 150words)
